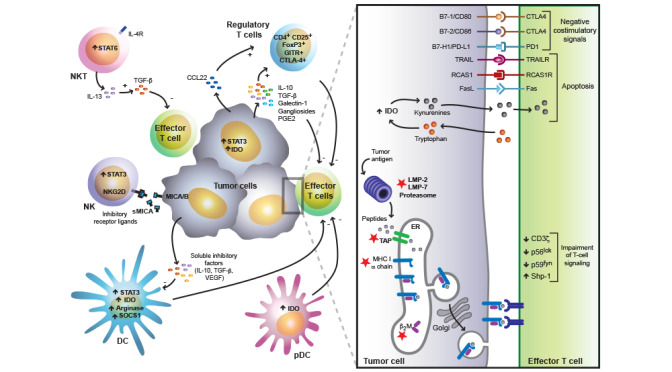
Immunosuppressive strategies and immunological checkpoints exploited by tumors to evade immune responses.
Tumors employ a plethora of immunosuppressive mechanisms, which may act in concert tocounteract effective immune responses.
Tumors employ a plethora of immunosuppressive mechanisms, which may act in concert to counteract effective immune responses. These include defects in T cell receptor (TCR) proximal signals, tumor induced impairment of the antigen presentation and processing machinery (red stars), activation of negative co-stimulatory signals in the tumor microenvironment (CTLA-4/B7, PD-1/PD-L1), elaboration of immunosuppressive factors (IL-10, TGF-β, galectin-1, gangliosides, PGE2), activation of pro-apoptotic pathways (FasL, TRAIL, IDO, RCAS1), inhibition of NK-cell mediated cytotoxicity (e.g release of soluble MICA) and inhibition of dendritic cell differentiation and maturation (STAT3, VEGF, IL-10, SOCS1, arginase). In addition, different regulatory cell populations contribute to this immunosuppressive network including CD4+CD25+ regulatory T-cells, inducible Tr1 cells, IL-13-producing NKT cells and distinct subsets of immature and mature myeloid and plasmacytoid DCs.
Rabinovich et al, Annu Rev Immunol. 2007